Computed radiography systems (CR system)
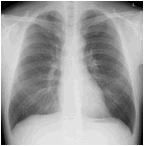
Images of the chest, abdomen, and whole body bones/joints are acquired with the CR system. It provides stable and clear images widely ranging from the soft parts to the bones as well.
CR uses an imaging plate instead of a film. After shooting, this system reads with the computer and performs digital processing to create an image.
Unlike a film, this is an eco-friendly technology because it can be performed multiple times with a single imaging plate.
A lifting bed is placed in the X-ray room so that people with disabilities, children, and elderly patients can get on and off safely without any burden.
We are constantly working toward the enhancement of the examination method to obtain a lot of information in a short time with less invasion so that there is no waiting time for the examination.
Digital X-ray fluoroscope with FPD system
X-ray fluoroscope
Hi-flexibility FPD Television System
Complete digitalization provides high quality image information with reduction in the imaging dose, various image processing, real-time image display, and consecutive photographing.
X-ray fluoroscopy examination (about representative examination in each department)
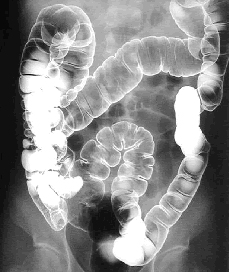
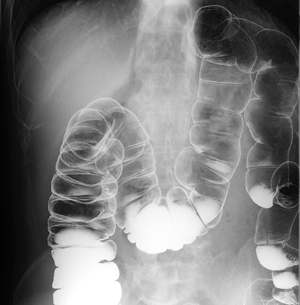
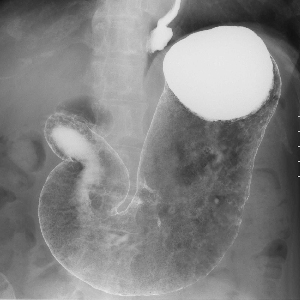
Gastrointestinal examination
Gastrointestinal examinations check if upper gastrointestinal angiography (the esophagus, stomach, and duodenum) and lower gastrointestinal angiography (colon) are normal.
Normally, a white liquid known as barium and air are injected or you are instructed to drink barium to attach it to the mucous membrane while the organs are inflated.
The state of the mucous membrane is reflected on the fluoroscope, and you can see if there is any abnormality.
Urological examination
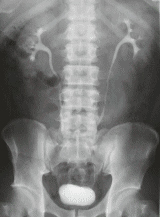
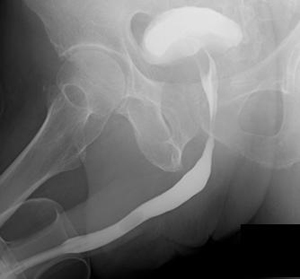
Excretory pyelography (DIP, IVP)
It is one of the common urological examinations to check the lesion, morphology, and function of the kidney, ureter, and bladder, etc. by injecting a contrast agent.
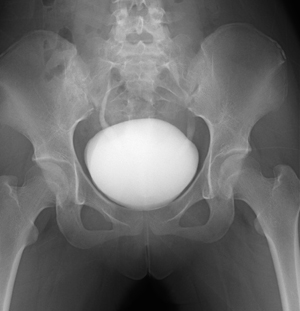
We perform cystography (CG), urinary cystography (VCG), urethral cystography (UCG), and chain CG.
These are tests to check the shape of a bladder and the degree of urinary incontinence by injecting a contrast agent into the bladder.
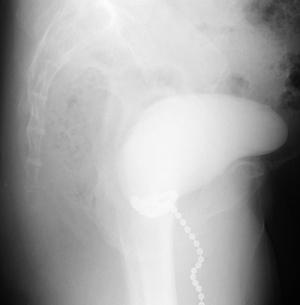
Gynecological examination
Hysterosalpingography (HSG)
This test is mainly used to check the cause of infertility.
A contrast agent is injected into uterine cavity to check the shape of the uterus and the passage of the fallopian tubes.
An equipment exclusively for gynecology is used for the examination.
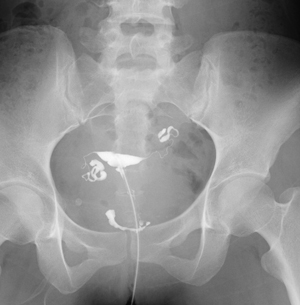
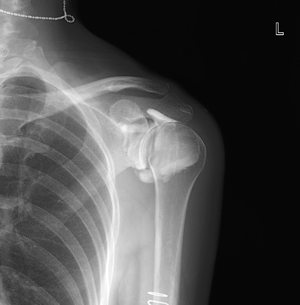
Orthopedic examination
Arthrography
A contrast agent is injected into a joint cavity in the joint (shoulder, hip, wrist, etc.) to examine the shape and damage of the joint cavity.
These include myelography, fracture reduction, dislocation reduction, and dynamic state examination (to check the joint movement).
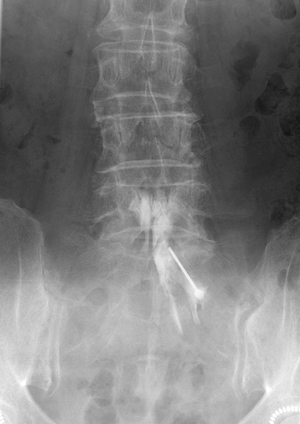
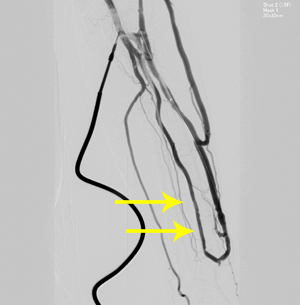
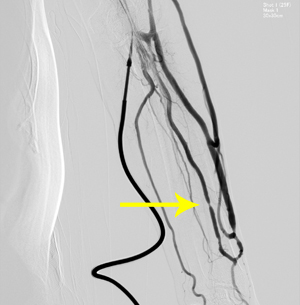
Angiography
A drug is directly injected into the blood vessels to check movement of the blood vessels and the constricted part. If there is a constricted part, we perform surgery to expand the narrow space with a small balloon.
A room and equipment exclusively for angiography are used for the examination.